A cut is usually caused by an encounter with a sharp object such as a knife or razor blade. Cuts can also happen on objects with thin edges such as paper or a thin cardboard box. A scratch is usually caused an abrasive surface such as sand paper, concrete and unfinished wood.
Children can get cuts and scratches once in a while, but are usually minor wounds and can be easily treated.
Symptoms
- Redness or swelling around the wound
- Bleeding
- Irritation or pain at the surface of the skin
Treatment
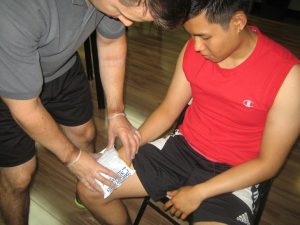
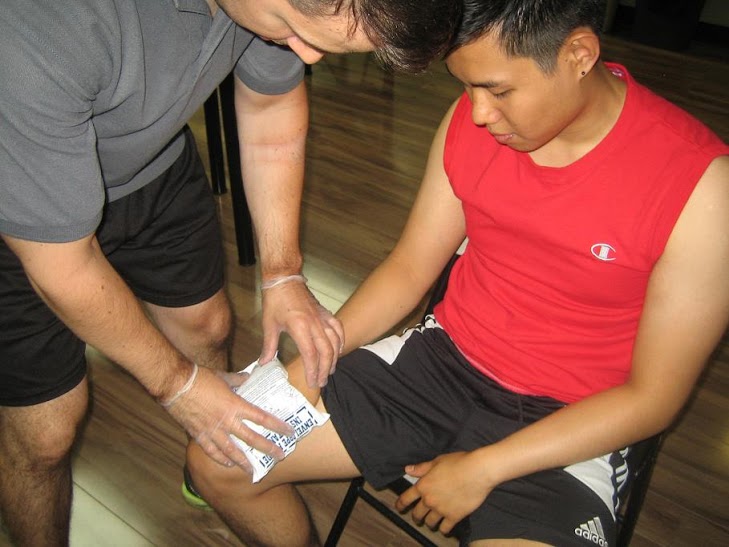
- Wash the hands before helping the affected child to prevent the wound from getting infected and allow the child sit or lie down.
- Clean the wound, if it is bleeding. Place sterile gauze or a clean cloth and apply firm pressure until the bleeding stops.
- Hold the affected area under cool running water and rub it gently using a clean cloth. Just remember to avoid using hot water. Bottled water or a saline wound spray can also be used in cleaning the wound. Avoid using iodine, alcohol, mercurochrome and hydrogen peroxide in cleaning the wound to minimize the irritation and pain.
- If the wound is not too deep but has debris or grit, clean the area using a pair of tweezers that has been sterilized with alcohol or boiling water to pick up the dirt and debris.
- Apply a cold compress or ice pack on the bruise at least for 20 minutes to prevent internal bleeding.
- Elevate the affected area for at least 15 minutes. Seek medical care if the bruise becomes worse.
- Apply the prescribed antibacterial cream or spray to prevent infection.
- Cover the wound using Band-Aid or sterile gauze to prevent infections. Utilize an adhesive or sticky bandage in covering the scrape or cut until it becomes dry and a scab has already formed. Take note that this help protect the fresh wound, lessen pain and oozing from wound.
Tips
- If the wound is deep, seek medical care for tetanus vaccination immediately.
- Cuts and scrapes that are in the healing process should not be exposed to sunlight to prevent markings or scarring of the affected area. Protect the affected area with clothing, dressing or applying sunscreen on the area.
- Maintain good skin care by applying a moisturizer and avoiding using harsh soaps or cleansers.
- Seek medical help immediately if bleeding cannot be stopped, the cut is deep, the cause of the cut or scrape an animal or human and cuts or scrapes that affects sensitive areas such as the eyes, face, genital or anal area.
- If signs of infections such as pain, fever, redness and pus are present, it is vital to seek medical help immediately.