Back pain is one of the most common complaints worldwide. Almost everyone will experience this type of pain at one point of their lives. In fact, it is a common reason for skipping work or going to a doctor. back ain is most common among adults between 35 and 55 years of age. It is not a disease on its own but rather, it is a symptom for a variety of underlying conditions.Back pain is usually not serious and typically goes away on their own even with minimal home treatment. There is rarely a need for surgery in cases of back pain.
Back pain can either be acute or chronic. Acute pain pertains to an abrupt pain that usually lasts for several days to a few weeks. On the other hand, chronic back pain is pain that lasts for more than three months. It is not generally advised to rest the back for more than one to two days as it may cause more harm.
Causes of Back Pain
As a common complaint, a wide range of conditions can lead to back pain. Some of the most common are the following:
- Structural problems
- Ruptured or bulging discs
- Arthritis
- Sciatica
- Scoliosis
- Osteoporosis
- Strain
- Strained muscles and ligaments
- Awkward posture in lifting heavy objects
- Muscle spasm
- Everyday activities
- Poor posture
- Overstretching
- Others
- Spine infection and other infections
- Spinal cancer
- Bad mattress
- Sleep disorder
Risk Factors for Back Pain
The following factors increase risks for developing back pain:
- Pregnancy
- Inactive lifestyle
- Strenuous physical activity and work
- Ageing
- Mentally stressful job
- Depression and anxiety
- Obesity
- Smoking
When to Seek Medical Care regarding Associated Symptoms with Back Pain
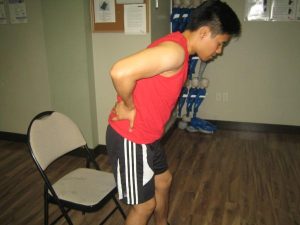
As the name suggests, the main symptom of back pain is aching anywhere in the back. However, it is most common in the lower back.
- Back pain that is not relieved even when resting or lying down
- Pain that radiates to the knees and legs
- Swollen back
- Loss of weight
- Fever
- Recent back injury
- Urinary incontinence or difficulty urinating
- Fecal incontinence
First Aid Management for Back Pain
In majority of back pain cases, it would typically go away on its own even without medical care and minimal home care. The following tips do not serve as medical advice or treatment. To learn how to properly treat and manage back pains, enrol in First Aid Courses offered by workplace approved all over the country.
- Rest but only do this for one to two days at most. Continue performing light activities such as, walking, to avoid completely immobilizing the back. If pain persists upon doing activities, stop performing the specific activity.
- Apply hot/ cold compresses to the affected area. For acute back pain, apply ice compress but for chronic back pain, apply hot compress.
- Take over-the-counter pain medications, such as paracetamol and ibuprofen, to help resolve back pains.
